Керамические предохранители (вставки плавкие) «Радиодеталь» для защиты оборудования
Защита электрического и электронного оборудования является необходимой не только в целях предотвращения выхода из строя, как правило, дорогостоящих устройств, но и также в целях предотвращения возникновения пожара и/или поражения пользователя электрическим током. Такая защита может быть реализована как внешними устройствами защиты в сети электропитания, например, автоматическими выключателями, так и элементами, встраиваемыми в конечное устройство. Одним из таких встраиваемых средств защиты является плавкий предохранитель или вставка плавкая.
Плавкий предохранитель включает в себя элемент – проводник с заданным сечением, который при протекании через него тока выше допустимого значения перегорает за счет нагрева до высокой температуры, или иным словом «плавится», то есть принцип действия предохранителя заложен в самом его названии. Плавкий предохранитель является самым слабым участком защищаемой электрической цепи – обычно входной, так как позволяет защитить от выхода из строя всё устройство целиком, в этом случае, при перегорании проводника в плавком предохранителе всё устройство полностью обесточивается.
Для корпусов плавких предохранителей (вставок) с малыми номинальными токами используются специальные стекла. Для более высоких номинальных токов корпуса обычно изготавливаются из высокопрочных сортов специальной керамики (фарфор, стеатит или корундо-муллитовая керамика). Также корпус выполняет функции камеры гашения электрической дуги.
 Внешний вид керамических плавких предохранителей «Радиодеталь»
Внешний вид керамических плавких предохранителей «Радиодеталь»
Одним из самых популярных производителей плавких предохранителей является отечественный завод «Радиодеталь», который выпускает широкий ассортимент предохранителей, их держателей и прочего электрооборудования. Среди плавких керамических предохранителей от завода «Радиодеталь» можно выделить следующие типы:
| Тип | Рабочий ток, А | Диапазон рабочей температуры, °С | Размеры, мм | Номер рисунка | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D | L | L1 | ||||
| ВП1-1 | 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 3.15, 4, 5 | -60…+100 | 4.0 | 15.0 | - | 1 |
| ВП1-2 | 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 3.15, 4, 5 | -60…+100 | 4.0 | 15.0 | 8.3 | 2 |
| ВП2Т-1Ш | 0.16, 0.2, 0.25, 0.315, 0.4, 0.5, 0.63, 0.8, 1.25, 1.6 | -60…+85 | 5.2 | 20.0 | 10.0 | 1 |
| ВП3Т-2Ш | 3.15, 4, 5, 6.3, 8, 10 | -60…+85 | 7.2 | 30.0 | 18.0 | 1 |
| ВП2Б-1В | 0.25, 0.5, 0.8, 1, 1.25, 1.6, 2, 2.5, 3.15, 4, 5, 6.3, 8, 10 250 | -60…+100 | 5.2 | 20.0 | 10.0 | 1 |
| ВП3Б-1В | 1, 1.25, 1.6, 2, 2.5, 3.15, 4, 5, 6.3, 8, 10 | -60…+100 | 7.2 | 30.0 | 18.0 | 1 |
| ВП4 | 0.1, 0.16, 0.2, 0.25, 0.315, 0.4, 0.5, 0.63, 0.75, 1, 1.25, 1.6, 2, 3.15, 3.5, 4, 5 | -60…+70 | 3.0 | 7.0 | 5.0 | 3 |
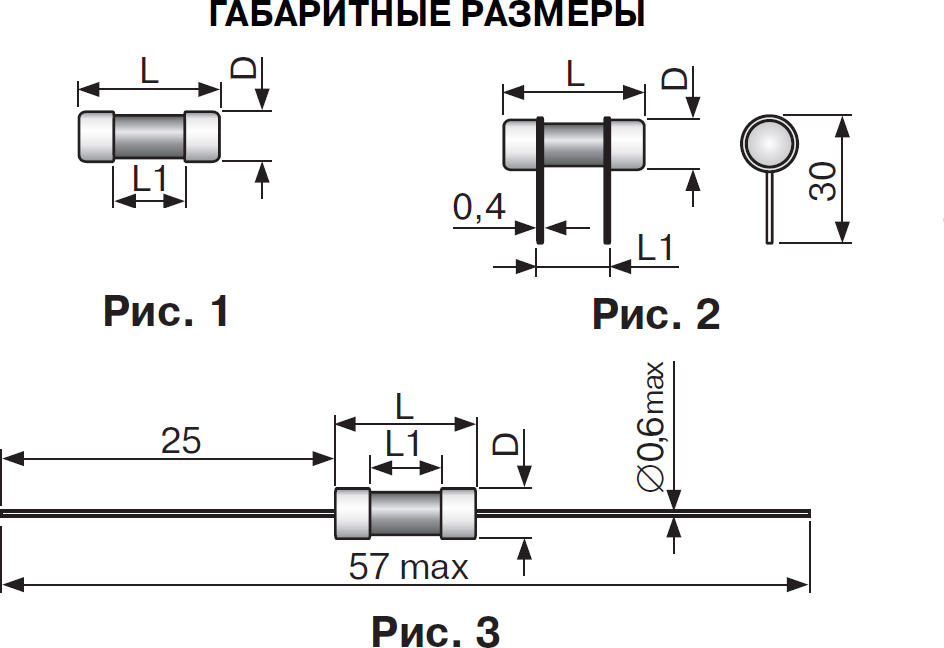 Габаритные размеры керамических предохранителей «Радиодеталь»
Габаритные размеры керамических предохранителей «Радиодеталь»
Рабочее напряжение всех представленных типов плавких предохранителей составляет 250В, то есть их основное предназначение – защита электрических устройств в однофазной сети переменного тока. Для предохранителей, предназначенных для использования в цепях переменного тока, в технических характеристиках указываются действующие значения токов и напряжений.
Более подробно технические характеристики плавких предохранителей можно узнать в Спецификациях на страничке товара.
